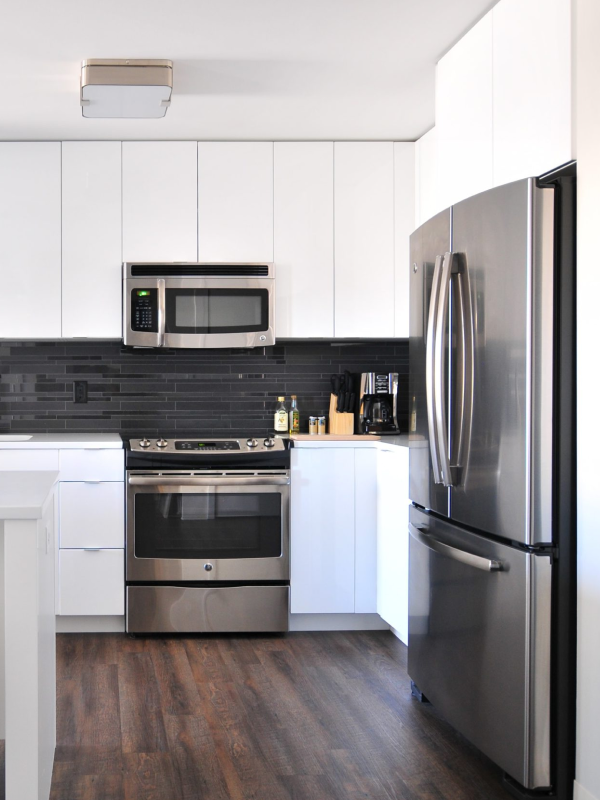
Nowadays, we are surrounded by hundreds of energy-hungry devices and appliances that promise to simplify our lives. From refrigerators and HVACs to washing machines and microwaves, these appliances have undoubtedly revolutionized our daily routines. However, behind the convenience lies a significant drawback - the substantial energy consumption that comes hand in hand with these power-hungry devices. Therefore, to know how much power these appliances consume, you should have proper knowledge of terms like wattage vs voltage vs amps.
Understanding these terminologies also aid you in identifying the extent of your energy consumption and its impact on your utility bills. You also get to know about how this excessive energy consumption is impacting the environment. Ready to know more about the basics of wattage, its calculation, and the difference between wattage vs voltage vs amps? Let's dive in!
- What is Wattage?
- Wattage vs Voltage vs Amps: What's the Difference?
- Some High Wattage Appliances
- EVVR Energy Monitoring Smart Plug and Relay - Detects All Your Energy-Hungry Appliances and Helps in Energy Efficiency
What is Wattage?
In wattage vs voltage vs amps, generally, wattage is known as the amount of power a device or appliance requires to run successfully. Wattage is expressed or measured in watts - equivalent to using one joule of energy per second. You must have proper knowledge about wattage or watts to find out the power requirements and consumption of your electrical appliances.
A device with a high wattage rating will consume more power, ultimately contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and increased energy bills. Following are some other power units that you should know to get a better understanding of your electricity bill and various appliance power consumption:
- Kilowatts - equal to 1000 watts and generally used for the power measurement of large appliances like dishwashers, refrigerators, etc.
- Megawatts - next on the list and are equal to one million watts or 1000 kilowatts. They are helpful in expressing the power capacity of larger systems or appliances like power plants, industrial facilities, and more.
- Gigawatts are the largest power units and comprise around one billion watts or thousand megawatts. They measure the power output of massive power plants, large-scale energy generation projects, or even a nation's energy consumption.
How to Calculate Wattage?
Want to know the wattage of your home? Collect information about the voltage or current flowing through a device and use the following formula to measure the wattage:
Wattage (W) = Voltage (V) × Current (I)
- Find the voltage (V) of the electrical circuit or device.
- Measure the current (I) flowing through the device, expressed in amperes (A).
Just multiply the voltage by the current, and you'll have the wattage. This makes this formula a wattage calculator. Consider the example of a device with a voltage of 120V and a current of 5A. Its wattage will be;
Wattage = 120V × 5A = 600W. Also, remember that wattage is an essential metric for understanding energy usage, managing electrical loads, and estimating electricity costs.
Wattage vs Voltage vs Amps: What's the Difference?
Voltage, wattage, and amps are among the most important electricity terms. To understand the nits and grits of the electricity system, you should know the basics of wattage vs voltage vs amps:

What is a Voltage?
Voltage measures the pressure the electric current requires to flow through a wire. It is also known as the measure of the potential difference between two points. Volt - the voltage unit - is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta, credited with inventing the voltaic pile. Remember that voltage is directly proportional to the flow of current, so when voltage increases, there's an increase in the current flow.
Different small appliances like light bulbs, TV, and others operate at 120V. Contrary to this, large appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, etc., use 240 V for proper operation. The formula for voltage calculation is given as follows:
Voltage = Wattage/Amps
If you have a device consuming 400 Watts and 20 Amps, the Voltage will be:
Voltage = 400/20 = 20V
Let's discuss the voltage level of various electrical systems:
|
Device |
Voltage Requirement |
|
USB |
5 |
|
Rechargeable Battery |
1.2 |
|
Automobile Battery |
2 |
|
Electric Vehicle Battery |
400 |
|
Non-Rechargeable Battery |
1.5 |
|
Lighting |
100,000,000 |
What are Amps?
In wattage vs voltage vs amps, we are now going to discuss the amps! Amperage, or you can say amps, is the measure of the electric current that flows through a circuit. Measured in Ampere, a name given after the French physicist André-Marie Ampère, who made significant contributions to the study of electromagnetism, it calculates the number of electrons passing through a point in the circuit per unit of time. Here's the formula to calculate amps:
Amps = Wattage/Voltage
The amps requirement of some appliances are:
|
Appliances |
Amps |
|
Water Pump |
11 |
|
Heater |
12.5 |
|
Fridge |
6.04 |
|
Dryer |
30 |
Wattage
Last and definitely not the list of wattage vs voltage vs amps is wattage (W). Named after James Watt, a Scottish engineer who made significant contributions to the development of the steam engine, wattage is the measure of the rate of electrical energy consumption or production in an electrical circuit. The formula for wattage calculation is given as follows:
Wattage (W) = Voltage (V) × Amps (A)
Here are some top appliances with their wattage requirement:
|
Devices |
Wattage |
|
Water Pump |
3000 W |
|
Heater |
1500 W |
|
Fridge |
1000 W |
|
Hair Dryer |
1200 W |
Some High Wattage Appliances
Now that you are well aware of the difference in wattage vs voltage vs amps, it's time to discuss some high wattage appliances in your home:

1. Electric Water Heater
As a resident of any of the coldest US states, you must have an electric water heater. This appliance aids you in performing various tasks, such as bathing, washing dishes, and more. There's convenience, but electric water heaters are also among the high-wattage appliances and consume a substantial amount of electricity. Usually, you can expect an electric water heater in your home will consume around 4000 Watts of electricity.
2. Refrigerators
Refrigerators are a part of every home, keeping food fresh and preventing spoilage. They run continuously and use electricity to maintain a cool temperature inside. Refrigerator wattage varies from anywhere between 300 W to 800 W. Newer models come with improved energy efficiency, but larger and older fridges still tend to consume more power. That's why it's suggested that you should choose an ENERGY STAR-rated or a smart refrigerator to save on your energy bills and reduce overall environmental impact.
3. Cooling Appliances
Imagine coming home during hot weather and being welcomed by high humidity and blazing hot temperatures. Sounds scary, no? That's where air conditioners and dehumidifiers got you!
They help maintain a cool and comfortable indoor environment during hot and humid weather. But if you are using a traditional cooling appliance with no smart features or energy star rating, you may feel the pressure of high electricity bills. Cooling devices are also among the significant electricity consumers, especially when operating at high cooling levels.
On average, an air conditioner takes around 3000 Watts of energy per hour. Worry no more! Just go with smart Z-wave thermostats, proper insulation, and regular cooling appliance servicing to improve your energy efficiency. Not only this, but you can also try smart air conditioners, smart dehumidifiers, and more to keep a check on your energy usage.
4. Dishwasher
The dishwasher is a convenient and time-saving appliance commonly found in modern homes. It efficiently cleans and sanitizes dishes, glasses, and utensils, reducing the need for manual washing. Being a high-wattage appliance, dishwashers consume around 1200 to 2400 Watts of electricity during operation.
EVVR Energy Monitoring Smart Plug and Relay - Detects All Your Energy-Hungry Appliances and Helps in Energy Efficiency
The EVVR Energy Monitoring Smart Plug & Relay is an innovative device that enables you to monitor your energy usage and identify energy-hungry appliances effortlessly. With this information at your fingertips, you can make informed decisions to either replace these power-hungry devices or optimize their energy usage.
This efficient smart plug is compatible with Apple HomeKit, empowering you to remotely control and automate various electrical appliances using the EVVR App. You can even track real-time power data and historical energy use to predict energy behavior and work towards enhancing energy efficiency throughout your home.
Besides energy optimization and tracking, this smart plug connects with your traditional devices and makes them innovative. With its ability to handle currents up to 16 amps and support 2-core and 3-core cables, it is a versatile addition to your smart home setup. In addition, EVVR includes safety features like a unique tamper-proof shell design, overload, and thermal protection. Along with these, there's a ground connection design and a button lock function to ensure the safety of your loved ones. So, get ready and take your home automation level up with the EVVR Plug!
Key Features
- Control and automate devices remotely with Apple HomeKit
- Real-time power data and historical energy use tracking help predict energy behavior for increased efficiency
- Tamper-proof shell design for safety
- Compatible with voice assistants like Alexa, Siri for more convenience
- Overload and thermal protection to prevent accidents
- Magnetic Retention Relay for stable performance
- Compatible with 2-core and 3-core cables
Conclusion
Multiple energy-hungry devices are present in your home that you are unaware of. So to identify those devices and learn about their wattage requirements, you must know the difference between wattage vs voltage vs amps. These terminologies help you understand which appliances use the most energy in your home. You can turn those power-hungry devices off and save some bucks. However, the best and tried method to track your energy usage is the EVVR Energy Monitoring Smart Plug and Relay.
It gives you information about appliances that consume the most power and track your energy behavior. With this information, you get a chance to optimize your energy usage and save some bucks. EVVR plug also makes your traditional appliances smart and gives you remote control. So what are you waiting for? Now, try our EVVR home automation range (EVVR In-Wall Relay Switch, EVVR Hub, EVVR Center Lite, etc.)!